Archive for the 'Networking' Category
-
June 27, 2023
利用高速光学连接扩展人工智能基础设施
By Suhas Nayak, Senior Director of Solutions Marketing, Marvell

In the world of artificial intelligence (AI), where compute performance often steals the spotlight, there's an unsung hero working tirelessly behind the scenes. It's something that connects the dots and propels AI platforms to new frontiers. Welcome to the realm of optical connectivity, where data transfer becomes lightning-fast and AI's true potential is unleashed. But wait, before you dismiss the idea of optical connectivity as just another technical detail, let's pause and reflect. Think about it: every breakthrough in AI, every mind-bending innovation, is built on the shoulders of data—massive amounts of it. And to keep up with the insatiable appetite of AI workloads, we need more than just raw compute power. We need a seamless, high-speed highway that allows data to flow freely, powering AI platforms to conquer new challenges.
In this post, I’ll explain the importance of optical connectivity, particularly the role of DSP-based optical connectivity, in driving scalable AI platforms in the cloud. So, buckle up, get ready to embark on a journey where we unlock the true power of AI together.
-
June 13, 2023
FC-NVMe 成为 HPE 下一代块存储的主流
By Todd Owens, Field Marketing Director, Marvell
While Fibre Channel (FC) has been around for a couple of decades now, the Fibre Channel industry continues to develop the technology in ways that keep it in the forefront of the data center for shared storage connectivity. Always a reliable technology, continued innovations in performance, security and manageability have made Fibre Channel I/O the go-to connectivity option for business-critical applications that leverage the most advanced shared storage arrays.
A recent development that highlights the progress and significance of Fibre Channel is Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s (HPE) recent announcement of their latest offering in their Storage as a Service (SaaS) lineup with 32Gb Fibre Channel connectivity. HPE GreenLake for Block Storage MP powered by HPE Alletra Storage MP hardware features a next-generation platform connected to the storage area network (SAN) using either traditional SCSI-based FC or NVMe over FC connectivity. This innovative solution not only provides customers with highly scalable capabilities but also delivers cloud-like management, allowing HPE customers to consume block storage any way they desire – own and manage, outsource management, or consume on demand. HPE GreenLake for Block Storage powered by Alletra Storage MP
HPE GreenLake for Block Storage powered by Alletra Storage MPAt launch, HPE is providing FC connectivity for this storage system to the host servers and supporting both FC-SCSI and native FC-NVMe. HPE plans to provide additional connectivity options in the future, but the fact they prioritized FC connectivity speaks volumes of the customer demand for mature, reliable, and low latency FC technology.
-
February 21, 2023
Marvell 和 Aviz Networks 合作推动 SONiC 在云和企业数据中心的部署
By Kant Deshpande, Director, Product Management, Marvell
Disaggregation is the future
Disaggregation—the decoupling of hardware and software—is arguably the future of networking. Disaggregation lets customers select best-of-breed hardware and software, enabling rapid innovation by separating the hardware and software development paths.Disaggregation started with server virtualization and is being adapted to storage and networking technology. In networking, disaggregation promises that any networking operating system (NOS) can be integrated with any switch silicon. Open source-standards like ONIE allow a networking switch to load and install any NOS during the boot process.
SONiC: the Linux of networking OS
Software for Open Networking in Cloud (SONiC) has been gaining momentum as the preferred open-source cloud-scale network operating system (NOS).In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2025, 40% of organizations that operate large data center networks (greater than 200 switches) will run SONiC in a production environment.[i] According to Gartner, due to readily expanding customer interest and a commercial ecosystem, there is a strong possibility SONiC will become analogous to Linux for networking operating systems in next three to six years.
-
February 14, 2023
下一代数据中心网络化需要做的三件事
By Amit Sanyal, Senior Director, Product Marketing, Marvell
Data centers are arguably the most important buildings in the world. Virtually everything we do—from ordinary business transactions to keeping in touch with relatives and friends—is accomplished, or at least assisted, by racks of equipment in large, low-slung facilities.
And whether they know it or not, your family and friends are causing data center operators to spend more money. But it’s for a good cause: it allows your family and friends (and you) to continue their voracious consumption, purchasing and sharing of every kind of content—via the cloud.
Of course, it’s not only the personal habits of your family and friends that are causing operators to spend. The enterprise is equally responsible. They’re collecting data like never before, storing it in data lakes and applying analytics and machine learning tools—both to improve user experience, via recommendations, for example, and to process and analyze that data for economic gain. This is on top of the relentless, expanding adoption of cloud services.
-
January 04, 2023
软件定义车辆的软件定义网络
By Amir Bar-Niv, VP of Marketing, Automotive Business Unit, Marvell and John Heinlein, Chief Marketing Officer, Sonatus and Simon Edelhaus, VP SW, Automotive Business Unit, Marvell
The software-defined vehicle (SDV) is one of the newest and most interesting megatrends in the automotive industry. As we discussed in a previous blog, the reason that this new architectural—and business—model will be successful is the advantages it offers to all stakeholders:
- The OEMs (car manufacturers) will gain new revenue streams from aftermarket services and new applications;
- The car owners will easily upgrade their vehicle features and functions; and
- The mobile operators will profit from increased vehicle data consumption driven by new applications.
What is a software-defined vehicle? While there is no official definition, the term reflects the change in the way software is being used in vehicle design to enable flexibility and extensibility. To better understand the software-defined vehicle, it helps to first examine the current approach.
Today’s embedded control units (ECUs) that manage car functions do include software, however, the software in each ECU is often incompatible with and isolated from other modules. When updates are required, the vehicle owner must visit the dealer service center, which inconveniences the owner and is costly for the manufacturer.
-
December 05, 2022
Leading Lights Award 对 Deneb CDSP 的佼佼者地位予以肯定
By Johnny Truong, Senior Manager, Public Relations, Marvell
 At this weeks’ Leading Lights Awards Ceremony, hosted by Light Reading, Editor-in-Chief Phil Harvey announced that the Marvell® Deneb™ Coherent Digital Signal Processor (CDSP) is the winner of the Most Innovative Service Provider Transport Solution category. This recognition is awarded to the optical systems vendor or optical components vendor providing the most innovative optical transport solution for service provider customers.
At this weeks’ Leading Lights Awards Ceremony, hosted by Light Reading, Editor-in-Chief Phil Harvey announced that the Marvell® Deneb™ Coherent Digital Signal Processor (CDSP) is the winner of the Most Innovative Service Provider Transport Solution category. This recognition is awarded to the optical systems vendor or optical components vendor providing the most innovative optical transport solution for service provider customers.Driving the industry's largest standards-based ecosystem, the Marvell Deneb CDSP enables disaggregation which is critical for carriers to lower their CAPEX and OPEX as they increase network capacity. This recognition underscores Marvell’s success in bringing leading-edge density and performance optimization advantages to carrier networks.
In its 18th year, the Leading Lights is Light Reading’s flagship awards program which recognizes top companies and executives for their outstanding achievements in next-generation communications technology, applications, services, strategies, and innovations.
Visit the Light Reading blog for a full list of categories, finalists and winners.
-
November 28, 2022
真正了不起的黑客 – 赢得 SONiC 用户满意
By Kishore Atreya, Director of Product Management, Marvell
Recently the Linux Foundation hosted its annual ONE Summit for open networking, edge projects and solutions. For the first time, this year’s event included a “mini-summit” for SONiC, an open source networking operating system targeted for data center applications that’s been widely adopted by cloud customers. A variety of industry members gave presentations, including Marvell’s very own Vijay Vyas Mohan, who presented on the topic of Extensible Platform Serdes Libraries. In addition, the SONiC mini-summit included a hackathon to motivate users and developers to innovate new ways to solve customer problems.
So, what could we hack?
At Marvell, we believe that SONiC has utility not only for the data center, but to enable solutions that span from edge to cloud. Because it’s a data center NOS, SONiC is not optimized for edge use cases. It requires an expensive bill of materials to run, including a powerful CPU, a minimum of 8 to 16GB DDR, and an SSD. In the data center environment, these HW resources contribute less to the BOM cost than do the optics and switch ASIC. However, for edge use cases with 1G to 10G interfaces, the cost of the processor complex, primarily driven by the NOS, can be a much more significant contributor to overall system cost. For edge disaggregation with SONiC to be viable, the hardware cost needs to be comparable to that of a typical OEM-based solution. Today, that’s not possible.
-
November 08, 2022
TSN 和 Prestera DX1500: 跨越 IT/OT 鸿沟的桥梁
By Reza Eltejaein, Director, Product Marketing, Marvell
Manufacturers, power utilities and other industrial companies stand to gain the most in digital transformation. Manufacturing and construction industries account for 37 percent of total energy used globally*, for instance, more than any other sector. By fine-tuning operations with AI, some manufacturers can reduce carbon emission by up to 20 percent and save millions of dollars in the process.
Industry, however, remains relatively un-digitized and gaps often exist between operational technology – the robots, furnaces and other equipment on factory floors—and the servers and storage systems that make up a company’s IT footprint. Without that linkage, organizations can’t take advantage of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies, also referred to as Industry 4.0. Of the 232.6 million pieces of fixed industrial equipment installed in 2020, only 10 percent were IIoT-enabled.
Why the gap? IT often hasn’t been good enough. Plants operate on exacting specifications. Engineers and plant managers need a “live” picture of operations with continual updates on temperature, pressure, power consumption and other variables from hundreds, if not thousands, of devices. Dropped, corrupted or mis-transmitted data can lead to unanticipated downtime—a $50 billion year problem—as well as injuries, blackouts, and even explosions.
To date, getting around these problems has required industrial applications to build around proprietary standards and/or complex component sets. These systems work—and work well—but they are largely cut off from the digital transformation unfolding outside the factory walls.
The new Prestera® DX1500 switch family is aimed squarely at bridging this divide, with Marvell extending its modern borderless enterprise offering into industrial applications. Based on the IEEE 802.1AS-2020 standard for Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN), Prestera DX1500 combines the performance requirements of industry with the economies of scale and pace of innovation of standards-based Ethernet technology. Additionally, we integrated the CPU and the switch—and in some models the PHY—into a single chip to dramatically reduce power, board space and design complexity.
Done right, TSN will lower the CapEx and OpEx for industrial technology, open the door to integrating Industry 4.0 practices and simplify the process of bringing new equipment to market. -
August 31, 2020
By Raghib Hussain, President, Products and Technologies
-
August 27, 2020
如何在 2020 年获得 NVMe over Fabric 的优势
By Todd Owens, Field Marketing Director, Marvell
As native Non-volatile Memory Express (NVMe®) share-storage arrays continue enhancing our ability to store and access more information faster across a much bigger network, customers of all sizes – enterprise, mid-market and SMBs – confront a common question: what is required to take advantage of this quantum leap forward in speed and capacity?
NVMe provides an efficient command set that is specific to memory-based storage, provides increased performance that is designed to run over PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0 bus architectures, and -- offering 64,000 command queues with 64,000 commands per queue -- can provide much more scalability than other storage protocols.
-
July 28, 2020
实现网络处理边缘化: 安全
By Alik Fishman, Director of Product Management, Marvell

我们在先前的“实现网络处理边缘化”系列中探讨了将智能、性能和遥测向网络边缘推进的相关趋势。 本部分将介绍网络安全的角色转变,以及将安全功能整合至网络接入的方法。这些方法可以在整个基础设施内有效推动策略实施、保护和修复的简化。
随着移动设备和物联网设备等新数据源在工作场所的快速普及,遭黑客攻击和遭泄露的数据数量也迅猛增长。不少企业深受其害,网络安全威胁成为困扰他们的日常难题。 安全漏洞也呈现新的发展趋势,不但数量持续上升,严重性和持续时间也在增长,从入侵到控制的平均生命周期长达近一年,1给运营带来巨大的成本压力。 而数字化转型和新兴技术格局(远程访问、云原生模型、物联网设备激增等)的出现,使网络架构和运营受到巨大影响,也催生出新的安全风险。 大刀阔斧地变革企业基础设施,提升网络智能、性能、可视性和安全性2,已经刻不容缓。
-
July 23, 2020
遥测: 您的边缘可见性如何?
作者:软件工程高级总监 Suresh Ravindran

我们在先前的“利用网络边缘计算”系列中探讨了将智能和性能向网络边缘推进的相关趋势。 这篇博客将谈谈对于网络可见性的需求。
随着自动化趋势不断演进,互联设备数量呈现 爆炸式增长。 据 IDC 估计,到 2025 年将有 416 亿台设备 连接至物联网 (loT),生成多达 79.4 泽字节的海量数据1。 视频流和 传感器流量在这类流量中将占到相当大的比例, 需针对混合云模式中的个性化用户服务、 库存管理、入侵防护和负载平衡等应用进行 智能处理。 联网设备将需要具备智能管理 资源处理的能力,才能高效地处理 海量数据流。
-
July 16, 2020
对边缘速度的需求
作者:Marvell 公司资深架构师 George Hervey

在之前的实现网络处理边缘化的相关提示中,我们了解到推动网络智能边缘化发展的趋势。 通过 5G 等崭新无线网络技术 所赋予的容量, 这种基础设施将有力推动创新型应用的开发。 此类应用 大多采用高频活动模型,例如视频或传感器, 其中的活动通常由设备自行发起,从而产生大量 跨网络基础设施传输的数据。 思科的 VNI 预测要闻预计, 2017 到 2022 年,全球移动数据流量将增长 6 倍,或相当于 42% 的年增长速度1,网络性能升级成为需求趋势。
-
July 08, 2020
推动网络智能和相关处理边缘化发展
作者:Marvell 公司资深架构师 George Hervey

随着我们迈向“永远在线,始终连接”(Always On,Always Connected)模式的更高阶段,手机已然成为我们生活中的核心部分。 手机为我们提供对数据和通信媒介的即时访问,这种方式的访问影响着我们的决定,并最终影响我们的行为。
据思科预计,到 2022 年,全球移动网络将支持超过 120 亿台移动设备和物联网 (loT) 连接。1 这些移动设备将支持多种功能。 手机已经取代了各种小工具,为我们提供多种服务。 如果手机可以提供 Apple Pay、Google Pay 或电子支付功能,即没有必要随身携带钱包。 如果手机可以解锁并启动汽车或打开车库门,即没有必要随身携带车钥匙。 现在,应用程序还包括实时流媒体服务,这些服务可支持 VR/AR 体验和实时共享。 未来的移动服务和应用程序似乎充满各种可能,它们依然需要下一代数据基础架构来支持和促进其发展。 -
April 02, 2018
理解当今的网络遥测需求
作者:Tal Mizrahi,Marvell 特征定义架构师
最近几年,网络实施的方式发生根本变化,随着数据需求的增长,类型更广泛的功能和运行性能水平的提高已经成为一种必要条件。 与之相伴的是另一种更大的需求,即针对该项性能标准的实时准确测量方式,以及深度分析,以便在任何潜在问题发展升级之前,查找并后续进行解决。
当今的数据网络发展速度不断加快且复杂性不断攀升,意味着对这类活动的监控进程难度越来越大。 结果导致只能强制执行更加繁琐且本质灵活的遥测机制,尤其是对于数据中心和企业网络。
当人们试图提取遥测资料时,发现有范围广大的多种不同选项,包括被动监控、主动测量和混合方法。 最普遍的一种做法是骑肩跟随遥测信息进入正在通过网络的数据包。 这种策略应用于原处 OAM (IOAM) 和带内网络遥测 (INT),以及替代进行的性能测量 (AM-PM) 背景之下。
Marvell 的方法是提供多样化且通用性高的工具组,可以通过它执行各种各样的遥测方法,而非局限于一种特定的测量协议。 欲了解此主题的更多信息,包括长久以来普遍所用的被动和主动测量协议,以及崭新的混合型遥测方法,请观看以下视频并下载 Marvell 白皮书。
-
February 22, 2018
Marvell 在世界移动大会 2018 上展示 CyberTAN White Box 解决方案,该方案搭载 Marvell ARMADA 8040 SoC、运行 Telco Systems NFVTime 通用 CPE OS
By Maen Suleiman, Senior Software Product Line Manager, Marvel
随着更多的工作负载转移到网络边缘,Marvell 进一步推进技术发展,让通讯行业可以从网络功能虚拟化 (NFV) 获取优势条件,充分利用其巨大潜力。 At this year’s Mobile World Congress (Barcelona, 26th Feb to 1st Mar 2018), Marvell, along with some of its key technology collaborators, will be demonstrating a universal CPE (uCPE) solution that will enable telecom operators, service providers and enterprises to deploy needed virtual network functions (VNFs) to support their customers’ demands.
ARMADA® 8040 uCPE 解决方案是多个 ARMADA 边缘计算解决方案中的一个,该产品即将上市,展示地点位于 Arm 展位(6 号厅 6E30 展位),将运行 Telco Systems NFVTime uCPE 操作系统 (OS),带有两个已部署好的现有 VNF(分别由 6WIND 和 Trend Micro 提供),可以实现虚拟路由和安全功能。 CyberTAN 白盒解决方案的设计是为了改变传统产品在具有性价比和系统能耗方面的不足,在非常大地改进这两方面因素的同时,保持非常高程度的安全性。
CyberTAN white box solution incorporating Marvell ARMADA 8040 SoC The CyberTAN white box platform is comprised of several key Marvell technologies that bring an integrated solution designed to enable significant hardware cost savings. 该平台集成以 Arm Cortex®-A72 四核处理器为基础的低功耗 Marvell® ARMADA 8040 系统单晶片 (SoC),具备高达 2GHz 的 CPU 时钟频率,还搭载 Marvell E6390x Link Street® 板上以太网交换机。 Marvell 以太网交换机支持 10G 上行链路和 8 个 1GbE 端口,并集成 PHY,其中四个是自动介质 GbE 端口(组合端口)。
CyberTAN 白盒得益于 Marvell ARMADA 8040 处理器的丰富功能组合以及强劲的软件生态系统,包含:
- 都是商业和工业级功能
- 双 10G 连接、10G 加密和 IPSEC 支持
- 服从 SBSA
- 支持 Arm TrustZone
- 支持包括下列在内范围广泛的多种软件: UEFI、Linux、DPDK、ODP、OPTEE、Yocto、OpenWrt、CentOS 等等
另外,uCPE 平台支持 Mini PCI Express (mPCIe) 扩展插槽,可以实现 Marvell 先进的 11ac/11ax Wi-Fi 或额外的有线/无线连接功能,还具备高达 16GB DDR4 DIMM、2 个 M.2 SATA、一个用于存储的 SATA 和 eMMC 选项,还有 SD 和 USB 扩展插槽可用于附加存储或其他有线/无线连接(例如 LTE)。
在 Arm 展位,Telco Systems 将在 CyberTAN 白盒上演示其 NFVTime uCPE 操作系统,及其零接触服务开通 (ZTP) 功能。 NFVTime 是一款直观的 NFVi-OS,可以辅助将 VNF 部署到 uCPE 的整个过程,同时避免复杂繁琐的管理和协调活动,一般会随之实现基于 NFV 的服务。 该项演示将包括两个主要的 VNF:
- 有一个 6WIND 虚拟路由器 VNF(基于 6WIND Turbo Router),可以提供很高的性能、即插即用的虚拟路由和防火墙功能;以及
- 一个 Trend Micro 安全 VNF(基于 Trend Micro 的虚拟功能网络套件 (VNFS)),可提供灵活的高性能网络安全功能,实现威胁防御和更有效、更快速的保护。
请联系您的 Marvell 销售代表,安排在世界移动大会期间会面,或在大会中莅临 Arm 展位(6 号厅 6E30 展位),亲眼见证 uCPE 解决方案的实施。
-
October 03, 2017
Wi-Fi 20 周年庆 - 第 1 篇
作者:Prabhu Loganathan,Marvell 互联事业部市场营销高级总监
You can't see it, touch it, or hear it - yet Wi-Fi® has had a tremendous impact on the modern world - and will continue to do so. From our home wireless networks, to offices and public spaces, the ubiquity of high speed connectivity without reliance on cables has radically changed the way computing happens. It would not be much of an exaggeration to say that because of ready access to Wi-Fi, we are consequently able to lead better lives - using our laptops, tablets and portable electronics goods in a far more straightforward, simplistic manner with a high degree of mobility, no longer having to worry about a complex tangle of wires tying us down.
This first in a series of blogs will look at the history of Wi-Fi to see how it has overcome numerous technical challenges and evolved into the ultra-fast, highly convenient wireless standard that we know today.
Unlicensed Beginnings
While we now think of 802.11 wireless technology as predominantly connecting our personal computing devices and smartphones to the Internet, it was in fact initially invented as a means to connect up humble cash registers. In the late 1980s, NCR Corporation, a maker of retail hardware and point-of-sale (PoS) computer systems, had a big problem. Its customers - department stores and supermarkets - didn't want to dig up their floors each time they changed their store layout.
They were set the challenge of creating a wireless communication protocol. These engineers succeeded in developing ‘WaveLAN’, which would be recognized as the precursor to Wi-Fi. Rather than preserving this as a purely proprietary protocol, NCR could see that by establishing it as a standard, the company would be able to position itself as a leader in the wireless connectivity market as it emerged.
Wireless Ethernet
Though the 802.11 wireless standard was released in 1997, it didn't take off immediately. Slow speeds and expensive hardware hampered its mass market appeal for quite a while - but things were destined to change. 10 Mbit/s Ethernet was the networking standard of the day. The IEEE 802.11 working group knew that if they could equal that, they would have a worthy wireless competitor. In 1999, they succeeded, creating 802.11b. This used the same 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band as the original 802.11 wireless standard, but it raised the throughput supported considerably, reaching 11 Mbits/s. Wireless Ethernet was finally a reality.
Thanks to cheaper equipment and better nominal ranges, 802.11b proved to be the most popular wireless standard by far. But, while it was more cost effective than 802.11a, 802.11b still wasn't at a low enough price bracket for the average consumer.
Apple was launching a new line of computers at that time and wanted to make wireless networking functionality part of it. The terms set were tough - Apple expected to have the cards at a $99 price point, but of course the volumes involved could potentially be huge.
PC makers saw Apple computers beating them to the punch and wanted wireless networking as well.
Working with engineers from Lucent, Microsoft made Wi-Fi connectivity native to the operating system. Users could get wirelessly connected without having to install third party drivers or software. With the release of Windows XP, Wi-Fi was now natively supported on millions of computers worldwide - it had officially made it into the ‘big time’.
-
July 17, 2017
合理精简以太网
作者:Marvell 公司资深架构师 George Hervey
Implementation of cloud infrastructure is occurring at a phenomenal rate, outpacing Moore's Law.
More and more switches are required, thereby increasing capital costs, as well as management complexity. To tackle the rising expense issues, network disaggregation has become an increasingly popular approach. By separating the switch hardware from the software that runs on it, vendor lock-in is reduced or even eliminated.
The number of managed switches basically stays the same.
Network Disaggregation
Almost every application we use today, whether at home or in the work environment, connects to the cloud in some way. Our email providers, mobile apps, company websites, virtualized desktops and servers, all run on servers in the cloud.
As demand increases, Moore's law has struggled to keep up. Scaling data centers today involves scaling out - buying more compute and storage capacity, and subsequently investing in the networking to connect it all.
Buying a switch, router or firewall from one vendor would require you to run their software on it as well. Larger cloud service providers saw an opportunity. These players often had no shortage of skilled software engineers.
802.1BR
Today's cloud data centers rely on a layered architecture, often in a fat-tree or leaf-spine structural arrangement. Rows of racks, each with top-of-rack (ToR) switches, are then connected to upstream switches on the network spine. The ToR switches are, in fact, performing simple aggregation of network traffic. Using relatively complex, energy consuming switches for this task results in a significant capital expense, as well as management costs and no shortage of headaches.
By replacing ToR switches with port extenders, port connectivity is extended directly from the rack to the upstream.
The Next Step in Network Disaggregation
Though many of the port extenders on the market today fulfill 802.1BR functionality, they do so using legacy components. Instead of being optimized for 802.1BR itself, they rely on traditional switches. This, as a consequence impacts upon the potential cost and power benefits that the new architecture offers.
Designed from the ground up for 802.1BR, Marvell's Passive Intelligent Port Extender (PIPE) offering is specifically optimized for this architecture. PIPE is interoperable with 802.1BR compliant upstream bridge switches from all the industry’s leading OEMs. It enables fan-less, cost efficient port extenders to be deployed, which thereby provide upfront savings as well as ongoing operational savings for cloud data centers.
802.1BR's port extender architecture is bringing about the second wave, where ports are decoupled from the switches which manage them.
-
July 07, 2017
延长基于 3.2T 交换机架构设备的生命周期
By Yaron Zimmerman, Senior Staff Product Line Manager, Marvell and Yaniv Kopelman, Networking and Connectivity CTO, Marvell
While network demands have increased, Moore's law (which effectively defines the semiconductor industry) has not been able to keep up. Instead of scaling at the silicon level, data centers have had to scale out. This has come at a cost though, with ever increasing capital, operational expenditure and greater latency all resulting. Facing this challenging environment, a different approach is going to have to be taken. In order to accommodate current expectations economically, while still also having the capacity for future growth, data centers (as we will see) need to move towards a modularized approach.
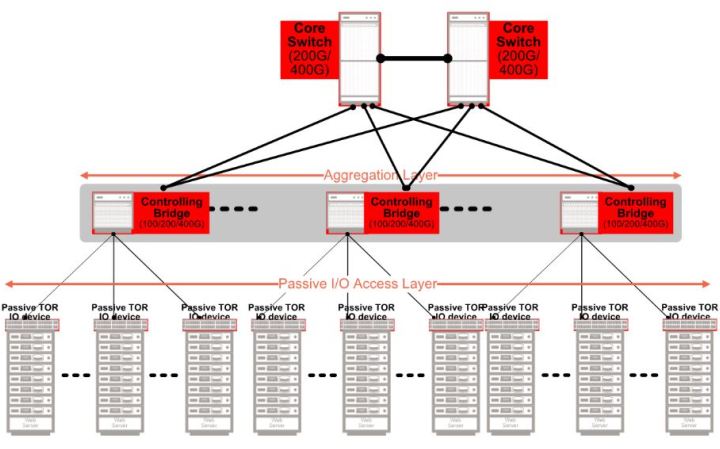 Scaling out the datacenter
Scaling out the datacenter Data centers are destined to have to contend with demands for substantially heightened network capacity - as a greater number of services, plus more data storage, start migrating to the cloud.
In turn these are consuming more power - which impacts on the overall power budget and means that less power is available for the data center servers. Not only does this lead to power being unnecessarily wasted, in addition it will push the associated thermal management costs and the overall Opex upwards. As these data centers scale out to meet demand, they're often having to add more complex hierarchical structures to their architecture as well - thereby increasing latencies for both north-south and east-west traffic in the process.
We used to enjoy cost reductions as process sizes decreased from 90 nm, to 65 nm, to 40 nm. That is no longer strictly true however. As we see process sizes go down from 28 nm node sizes, yields are decreasing and prices are consequently going up. To address the problems of cloud-scale data centers, traditional methods will not be applicable.
PIPEs and Bridges
Today's data centers often run on a multi-tiered leaf and spine hierarchy. Racks with ToR switches connect to the network spine switches. These, in turn, connect to core switches, which subsequently connect to the Internet.
By following a modularized approach, it is possible to remove the ToR switches and replace them with simple IO devices - port extenders specifically. This effectively extends the IO ports of the spine switch all the way down to the ToR. What results is a passive ToR that is unmanaged. It simply passes the packets to the spine switch.
The spine switch now acts as the controlling bridge. It is able to manage the layer which was previously taken care of by the ToR switch. This means that, through such an arrangement, it is possible to disaggregate the IO ports of the network that were previously located at the ToR switch, from the logic at the spine switch which manages them. This innovative modularized approach is being facilitated by the increasing number of Port Extenders and Control Bridges now being made available from Marvell that are compatible with the IEEE 802.1BR bridge port extension standard.
Solving Data Center Scaling Challenges
Port extenders solve the latency by flattening the hierarchy. Instead of having conventional ‘leaf’ and ‘spine’ tiers, the port extender acts to simply extend the IO ports of the spine switch to the ToR. Each server in the rack has a near-direct connection to the managing switch.
The passive port extender is a greatly simplified device compared to a managed switch. This means lower up-front costs as well as lower power consumption and a simpler network management scheme are all derived.
-
June 21, 2017
更好地利用原有的基础设施
By Ron Cates
The flexibility offered by wireless networking is revolutionizing the enterprise space. High-speed Wi-Fi®, provided by standards such as IEEE 802.11ac and 802.11ax, makes it possible to deliver next-generation services and applications to users in the office, no matter where they are working. However, the higher wireless speeds involved are putting pressure on the cabling infrastructure that supports the Wi-Fi access points around an office environment. The 1 Gbit/s Ethernet was more than adequate for older wireless standards and applications. Now, with greater reliance on the new generation of Wi-Fi access points and their higher uplink rate speeds, the older infrastructure is starting to show strain. At the same time, in the server room itself, demand for high-speed storage and faster virtualized servers is placing pressure on the performance levels offered by the core Ethernet cabling that connects these systems together and to the wider enterprise infrastructure. One option is to upgrade to a 10 Gbit/s Ethernet infrastructure. But this is a migration that can be prohibitively expensive. The Cat 5e cabling that exists in many office and industrial environments is not designed to cope with such elevated speeds. To make use of 10 Gbit/s equipment, that old cabling needs to come out and be replaced by a new copper infrastructure based on Cat 6a standards. Cat 6a cabling can support 10 Gbit/s Ethernet at the full range of 100 meters, and you would be lucky to run 10 Gbit/s at half that distance over a Cat 5e cable. In contrast to data-center environments that are designed to cope easily with both server and networking infrastructure upgrades, enterprise cabling lying in ducts, in ceilings and below floors is hard to reach and swap out. This is especially true if you want to keep the business running while the switchover takes place. Help is at hand with the emergence of the IEEE 802.3bz™ and NBASE-T® set of standards and the transceiver technology that goes with them. 802.3bz and NBASE-T make it possible to transmit at speeds of 2.5 Gbit/s or 5 Gbit/s across conventional Cat 5e or Cat 6 at distances up to the full 100 meters. The transceiver technology leverages advances in digital signal processing (DSP) to make these higher speeds possible without demanding a change in the cabling infrastructure. The NBASE-T technology, a companion to the IEEE 802.3bz standard, incorporates novel features such as downshift, which responds dynamically to interference from other sources in the cable bundle. The result is lower speed. But the downshift technology has the advantage that it does not cut off communication unexpectedly, providing time to diagnose the problem interferer in the bundle and perhaps reroute it to sit alongside less sensitive cables that may carry lower-speed signals. This is where the new generation of high-density transceivers come in. There are now transceivers coming onto the market that support data rates all the way from legacy 10 Mbit/s Ethernet up to the full 5 Gbit/s of 802.3bz/NBASE-T - and will auto-negotiate the most appropriate data rate with the downstream device. This makes it easy for enterprise users to upgrade the routers and switches that support their core network without demanding upgrades to all the client devices. Further features, such as Virtual Cable Tester® functionality, makes it easier to diagnose faults in the cabling infrastructure without resorting to the use of specialized network instrumentation. Transceivers and PHYs designed for switches can now support eight 802.3bz/NBASE-T ports in one chip, thanks to the integration made possible by leading-edge processes. These transceivers are designed not only to be more cost-effective, they also consume far less power and PCB real estate than PHYs that were designed for 10 Gbit/s networks. This means they present a much more optimized solution with numerous benefits from a financial, thermal and a logistical perspective. The result is a networking standard that meshes well with the needs of modern enterprise networks - and lets that network and the equipment evolve at its own pace. -
June 07, 2017
社区开发板允许在数据中心、网络和存储生态系统中轻松采用 ARM 64 位性能
作者:Maen Suleiman,Marvell 软件产品线高级经理
Marvell MACCHIATObin community board is first-of-its-kind, high-end ARM 64-bit networking and storage community board
The industry is answering that call through technologies and concepts such as software defined networking (SDN), network function virtualization (NFV) and distributed storage. Making the most of these technologies and unleashing the potential of the new applications requires a collaborative approach.
A key way to foster such collaboration is through open-source ecosystems. The rise of Linux has demonstrated the effectiveness of such ecosystems and has helped steer the industry towards adopting open-source solutions. AT&T Runs Open Source White Box Switch in its Live Network, SnapRoute and Dell EMC to Help Advance Linux Foundation's OpenSwitch Project, Nokia launches AirFrame Data Center for the Open Platform NFV community)
Communities have come together through Linux to provide additional value for the ecosystem. One example is the Linux Foundation Organization which currently sponsors more than 50 open source projects. Its activities cover various parts of the industry from IoT ( IoTivity , EdgeX Foundry ) to full NFV solutions, such as the Open Platform for NFV (OPNFV). This is something that would have been hard to conceive even a couple of years ago without the wide market acceptance of open-source communities and solutions.
Although there are numerous important open-source software projects for data-center applications, the hardware on which to run them and evaluate solutions has been in short supply. There are many ARM® development boards that have been developed and manufactured, but they primarily focus on simple applications.
All these open source software ecosystems require a development platform that can provide a high-performance central processing unit (CPU), high-speed network connectivity and large memory support. But they also need to be accessible and affordable to ARM developers. Marvell MACCHIATObin® is the first ARM 64-bit community platform for open-source software communities that provides solutions for, among others, SDN, NFV and Distributed Storage.
 A high-performance ARM 64-bit community platform
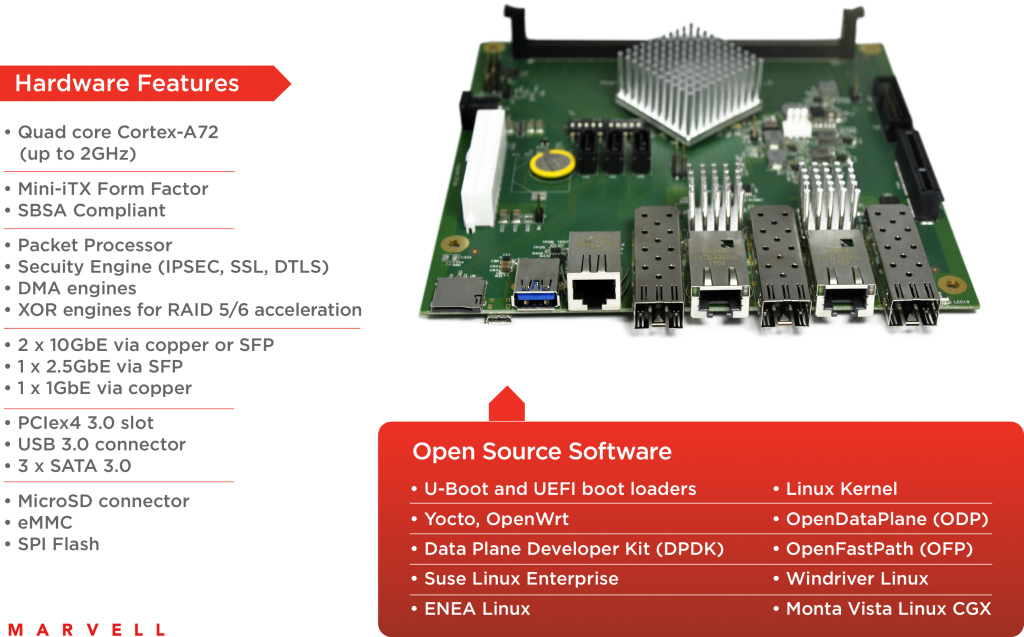
A high-performance ARM 64-bit community platform It is based on the Marvell hyperscale SBSA-compliant ARMADA® 8040 system on chip (SoC) that features four high-performance Cortex®-A72 ARM 64-bit CPUs.
SolidRun (https://www.solid-run.com/) started shipping the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board in March 2017, providing an early access of the hardware to open-source communities.
The Marvell MACCHIATObin community board is easy to deploy. It uses the compact mini-ITX form factor, enabling developers to purchase one of the many cases based on the popular standard mini-ITX case to meet their requirements. The ARMADA 8040 SoC itself is SBSA-compliant (http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0029/) to offer unified extensible firmware interface (UEFI) support.
In addition, the SoC provides two security engines that can perform full IPSEC, DTL and other protocol-offload functions at 10G rates.
For hardware expansion, the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board provides one PCIex4 3.0 slot and a USB3.0 host connector. For non-volatile storage, options include a built-in eMMC device and a micro-SD card connector. Mass storage is available through three SATA 3.0 connectors. For debug, developers can access the board’s processors through a choice of a virtual UART running over the microUSB connector, 20-pin connector for JTAG access or two UART headers. MACCHIATObin Specification.
Open source software enables advanced applications
The Marvell MACCHIATObin community board comes with rich open source software that includes ARM Trusted Firmware (ATF), U-Boot, UEFI, Linux Kernel, Yocto, OpenWrt, OpenDataPlane (ODP) , Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK), netmap and others; many of the Marvell MACCHIATObin open source software core components are available at: https://github.com/orgs/MarvellEmbeddedProcessors/.
To provide the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board with ready-made support for the open-source platforms used at the edge and data centers for SDN, NFV and similar applications, standard operating systems like Suse Linux Enterprise, CentOS, Ubuntu and others should boot and run seamlessly on the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board.
As the ARMADA 8040 SoC is SBSA compliant and supports UEFI with ACPI, along with Marvell’s upstreaming of Linux kernel support, standard operating systems can be enabled on the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board without the need of special porting.
On top of this core software, a wide variety of ecosystem applications needed for the data center and edge applications can be assembled.
For example, using the ARMADA 8040 SoC high-speed networking and security engine will enable the kernel netdev community to develop and maintain features such as XDP or other kernel network features on ARM 64-bit platforms. The ARMADA 8040 SoC security engine will enable many other Linux kernel open-source communities to implement new offloads.
Thanks to the virtualization support available on the ARM Cortex A72 processors, virtualization technology projects such as KVM and XEN can be enabled on the platform; container technologies like LXC and Docker can also be enabled to maximize data center flexibility and enable a virtual CPE ecosystem where the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board can be used to develop edge applications on a 64-bit ARM platform.
In addition to the mainline Linux kernel, Marvell is upstreaming U-Boot and UEFI, and is set to upstream and open the Marvell MACCHIATObin ODP and DPDK support. This makes the Marvell MACCHIATObin board an ideal community platform for both communities, and will open the door to related communities who have based their ecosystems on ODP or DPDK. These may be user-space network-stack communities such as OpenFastPath and FD.io or virtual switching technologies that can make use of both the ARMADA 8040 SoC virtualization support and networking capabilities such as Open vSwitch (OVS) or Vector Packet Processing (VPP). Similar to ODP and DPDK, Marvell MACCHIATObin netmap support can enable VALE virtual switching technology or security ecosystem such as pfsense.
Thanks to its hardware features and upstreamed software support, the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board is not limited to data center SDN and NFV applications. It is highly suited as a development platform for network and security products and applications such as network routers, security appliances, IoT gateways, industrial computing, home customer-provided equipment (CPE) platforms and wireless backhaul controllers; a new level of scalable and modular solutions can be further achieved when combining the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board with Marvell switches and PHY products.
Summary
The board supports a rich software ecosystem and has made available high-performance, high-speed networking ARM 64-bit community platforms at a price that is affordable for the majority of ARM developers, software vendors and other interested companies.
-
2017 年 5 月 23 日
Marvell MACCHIATObin 社区开发板开始发货
作者:Maen Suleiman,Marvell 软件产品线高级经理
First-of-its-kind community platform makes ARM-64bit accessible for data center, networking and storage solutions developers
Now, with the shipping of the Marvell MACCHIATObin™ community board, developers and companies have access to a high-performance, affordable ARM®-based platform with the required technologies such as an ARMv8 64bit CPU, virtualization, high-speed networking and security accelerators, and the added benefit of open source software. SolidRun started shipping the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board in March 2017, providing an early access of the hardware to open-source communities.
Click image to enlarge
The Marvell MACCHIATObin community board is a mini-ITX form-factor ARMv8 64bit network- and storage-oriented community platform. It is based on the Marvell® hyperscale SBSA-compliant ARMADA® 8040 system on chip (SoC) (http://www.marvell.com/embedded-processors/armada-80xx/) that features quad-core high-performance Cortex®-A72 ARM 64bit CPUs
This power does not come at the cost of affordability: the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board is priced at $349.
The Marvell MACCHIATObin community board is easy to deploy. It uses the compact mini-ITX form factor enabling developers and companies to purchase one of the many cases based on the popular standard mini-ITX case to meet their requirements. The ARMADA 8040 SoC itself is SBSA- compliant to offer unified extensible firmware interface (UEFI) support. You can find the full specification at: http://wiki.macchiatobin.net/tiki-index.php?page=About+MACCHIATObin.
To provide the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board with ready-made support for the open-source platforms used in SDN, NFV and similar applications, Marvell is upstreaming MACCHIATObin software support to the Linux kernel, U-Boot and UEFI, and is set to upstream and open the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board for ODP and DPDK support.
In addition to upstreaming the MACCHIATObin software support, Marvell added MACCHIATObin support to the ARMADA 8040 SDK and plans to make the ARMADA 8040 SDK publicly available. Many of the ARMADA 8040 SDK components are available at: https://github.com/orgs/MarvellEmbeddedProcessors/.
For more information about the many innovative features of the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board, please visit: http://wiki.macchiatobin.net. To place an order for the Marvell MACCHIATObin community board, please go to: http://macchiatobin.net/.
-
April 27, 2017
11ac Wave 2 和 11ax 在 Wi-Fi 部署中的挑战: 如何经济高效地升级到 2.5GBASE-T 和 5GBASE-T
By Nick Ilyadis
IEEE has also noted that in the past two decades, the IEEE 802.11 wireless local area networks (WLANs) have also experienced tremendous growth with the proliferation of IEEE 802.11 devices, as a major Internet access for mobile computing. Therefore, the IEEE 802.11ax specification is under development as well. Giving equal time to Wikipedia, its definition of 802.11ax is: a type of WLAN designed to improve overall spectral efficiency in dense deployment scenarios, with a predicted top speed of around 10 Gbps. It works in 2.4GHz or 5GHz and in addition to MIMO and MU-MIMO, it introduces Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) technique to improve spectral efficiency and also higher order 1024 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) modulation support for better throughputs. Though the nominal data rate is just 37 percent higher compared to 802.11ac, the new amendment will allow a 4X increase of user throughput. This new specification is due to be publicly released in 2019.
Faster “Cats” Cat 5, 5e, 6, 6e and on
And yes, even cabling is moving up to keep up. Differences between CAT5, CAT5e, CAT6 and CAT6e Cables for specifics), but suffice it to say, each iteration is capable of moving more data faster, starting with the ubiquitous Cat 5 at 100Mbps at 100MHz over 100 meters of cabling to Cat 6e reaching 10,000 Mbps at 500MHz over 100 meters. Cat 7 can operate at 600MHz over 100 meters, with more “Cats” on the way. All of this of course, is to keep up with streaming, communications, mega data or anything else being thrown at the network.
How to Keep Up Cost-Effectively with 2.5BASE-T and 5BASE-T
This is where Marvell steps in with a whole solution. Marvell’s products, including the Avastar wireless products, Alaska PHYs and Prestera switches, provide an optimized solution that will help support up to 2.5 and 5.0 Gbps speeds, using existing cabling. For example, the Marvell Avastar 88W8997 wireless processor was the industry's first 28nm, 11ac (wave-2), 2x2 MU-MIMO combo with full support for Bluetooth 4.2, and future BT5.0. To address switching, Marvell created the Marvell® Prestera® DX family of packet processors, which enables secure, high-density and intelligent 10GbE/2.5GbE/1GbE switching solutions at the access/edge and aggregation layers of Campus, Industrial, Small Medium Business (SMB) and Service Provider networks. And finally, the Marvell Alaska family of Ethernet transceivers are PHY devices which feature the industry's lowest power, highest performance and smallest form factor.
These transceivers help optimize form factors, as well as multiple port and cable options, with efficient power consumption and simple plug-and-play functionality to offer the most advanced and complete PHY products to the broadband market to support 2.5G and 5G data rate over Cat5e and Cat6 cables.
You mean, I don’t have to leave the wiring closet?
# # #
-
April 27, 2017
如何解决数据中心对高带宽的饥渴,Marvell 谈数据中心八大发展趋势
作者:Nick Ilyadis,Marvell 产品线技术副总裁
IoT devices, online video streaming, increased throughput for servers and storage solutions – all have contributed to the massive explosion of data circulating through data centers and the increasing need for greater bandwidth. IT teams have been chartered with finding the solutions to support higher bandwidth to attain faster data speeds, yet must do it in the most cost-efficient way - a formidable task indeed. Marvell recently shared with eWeek about what it sees as the top trends in data centers as they try to keep up with the unprecedented demand for higher and higher bandwidth. Below are the top eight data center trends Marvell has identified as IT teams develop the blueprint for achieving high bandwidth, cost-effective solutions to keep up with explosive data growth.
Real-time analytics allow organizations to monitor and make adjustments as needed to effectively allocate precious network bandwidth and resources. Leveraging analytics has become a key tool for data center operators to maximize their investment.

能源成本往往是导致数据中心成本居高不下的主因。 Ethernet solutions designed with greater power efficiency help data centers transition to the higher GbE rates needed to keep up with the higher bandwidth demands, while keeping energy costs in check.

By using the NVMe protocol, data centers can exploit the full performance of SSDs, creating new compute models that no longer have the limitations of legacy rotational media. SSD performance can be maximized, while server clusters can be enabled to pool storage and share data access throughout the network.
 8.) Transition from Servers to Network Storage With the growing amount of data transferred across networks, more data centers are deploying storage on networks vs. servers.
8.) Transition from Servers to Network Storage With the growing amount of data transferred across networks, more data centers are deploying storage on networks vs. servers. # # #
-
April 03, 2017
手机的出现如何点燃当今的数据需求增长
作者:Sander Arts,Marvell 市场营销代理副总裁
1973 年 4 月 3 日,也就是大约 44 年以前,一位名叫 Martin Cooper 的工程师沿着曼哈顿的街道往前走,手里拿着个像砖头一样的设备,拨通了有史以来的第一次移动通话。 世界上第一部移动设备重量达到令人乍舌的 2.5 磅,高 11 英寸,突出特点是只有一条线路、只能发送短信的 LED 显示屏。

版权: 维基百科
从那以后发生了很多变化。 电话变得更小、更快,也更智能,以四十年前人们无法想象的速度更新换代。 今天,打电话只是我们期望移动设备承担的众多功能之一,此外它还要能上网浏览、观看视频、查找方位、参与社交,还有其他各种功能。 所有这些活动都要求数据的快速移动和存储,与最初的 PC 更加相似,而非 Cooper 的 2.5 磅原型机。 而且这还只是个开始,数据需求的增长比移动技术的更新换代更加迅速。
数据需求: 超越无限!
现今的消费者可以使用各种各样的设备,几乎瞬时读取来自全世界的内容,这些设备包括智能手机、平板电脑、汽车,甚至是家用电器。 不管是大型活动,比如超级碗 LI,还是普通的一天,数据使用量都在迅猛增长,人们跟朋友、家人和世界各地的陌生人交流,分享想法、上传照片、观看视频、玩游戏,还有很多其他的活动。
根据 Domo 所做的一项研究,在美国,消费者每分钟要使用超过 180 万兆字节无线数据。 在最近的 2017 美国 OCP 峰会上,Facebook 宣称每天会有 9500 万份照片和视频通过 Instagram 发布,而这还只是单独一个应用程序。随着我们的世界变得更加智能、连接程度更高,数据需求只会继续不断增长。
下一代数据移动和存储
在 Marvell,当我们在从消费者到云端的广阔市场范围中变革数据移动和存储方式,我们注重的是更加安全、可靠和高效的帮助客户移动和存储数据。 世界每天都会创建和移动数量惊人的数据,我们理所当然享受着现有的科技,几乎已经无法想象科技萌芽时期的笨拙。
我们未来的设备将承担何种功能来支持数据需求呢? 给我们在 Tweet 留言 @marvellsemi 告诉我们你的想法!
-
October 13, 2016
Marvell 推出业界新面世的充分兼容 IEEE 802.3by 25GbE 标准的 25G PHY 收发器
By Venu Balasubramonian, Marketing Director, Connectivity, Storage and Infrastructure Business Unit, Marvell
Alaska C 88X5123 enables adoption of 25G Ethernet in datacenters and enterprise networks
Growing demand for networking bandwidth is one of the biggest pain points facing datacenters today. To enable this, IEEE developed the 802.3by specifications defining Ethernet operation at 25Gbps, which was ratified recently. We are excited to introduce the high performance Marvell Alaska C 88X5123 Ethernet transceiver, the industry’s first PHY transceiver fully compliant to the new IEEE 25GbE specification.
The device is packaged in a small 17mm x 17mm package, and supports 8 ports of 25GbE, four ports of 50GbE or two ports of 100GbE operation.
For more information on Marvell’s Alaska C 88X5123 Ethernet transceiver, please visit: http://www.marvell.com/transceivers/alaska-c-gbe/
-
October 06, 2016
Marvell PHY,专为实现低延时工业以太网
By Kaushik Mittra, Senior Product Marketing Manager, Ethernet PHY products, Connectivity, Storage and Infrastructure Business Unit, Marvell
Part 1 of Two-Part Series
Introducing the Marvell 88E1510P/1512P/1510Q Family of PHY Products
Industrial networks present their own set of challenges, and Ethernet with its components are evolving again to address the needs of the factory floor. Connectivity hardware that can offer low-latency, enhanced electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection while operating in extended temperature environments is invaluable to industrial network implementation.
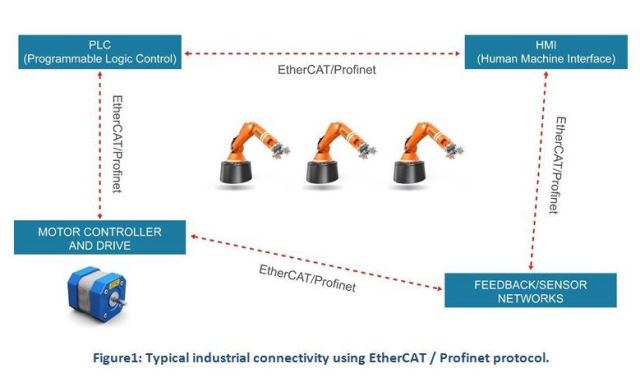
But what they share in common is the goal to deliver real-time Ethernet to industrial automation applications under harsh environmental conditions. The typical elements of an industrial network might include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), motor controllers and drives, sensor networks and human machine interfaces (HMIs). These elements are connected on the Ethernet backbone using a protocol such as EtherCAT or Profinet. The network topology might be hub-spoke (star) or linear. Regardless of network topology, the goal is to provide precise control and synchronized timing information to each of the nodes. If the topology is a long daisy chain, then each node has to perform with the most optimized latency to enable fast request/response cycle times through the system.
Looking for a Low-Latency PHY?
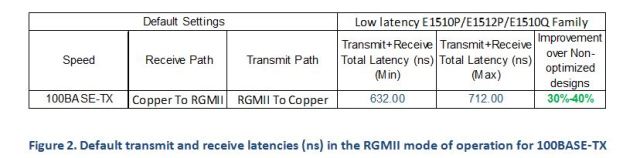
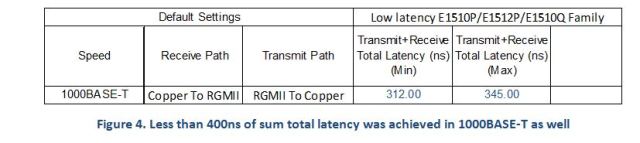
Protocols such as EtherCAT have to process the Ethernet packet and insert new data into the frame as it passes through in real-time. For real-time applications, this imposes tight restrictions on the latency through the switch and PHY. With this requirement in mind, we designed the Marvell 88E1510P/1512P/1510Q family of PHY products to address the stringent latency needs of tier-1 industrial customers. The table below shows that the Marvell low-latency PHY operates 30-40 percent faster as compared to non-optimized implementations.
 While the data shown above is the default configuration, significantly lower latencies are possible with register programming. The sum total of transmit and receive latency was less than 400ns across the entire range, as shown below.
While the data shown above is the default configuration, significantly lower latencies are possible with register programming. The sum total of transmit and receive latency was less than 400ns across the entire range, as shown below. 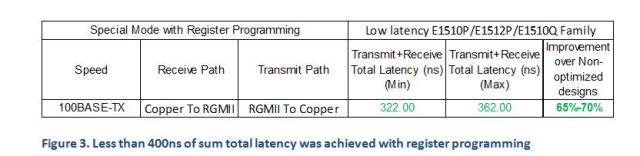 The small latency variation observed (from min to max) is due to the presence of synchronization circuits in the transmit path. Typically a FIFO (first in, first out queue) is used in the transmit path to compensate for any PPM (parts-per-million) differences between the transmit circuits and receiving circuits. Depending on packet size and the number of entries in the FIFO, a small variation in latency can be observed. (Note: When the PHY is used for precision-time protocol- (PTP-) based timestamping applications, the presence of the FIFO does not affect the accuracy of the timestamps.
The small latency variation observed (from min to max) is due to the presence of synchronization circuits in the transmit path. Typically a FIFO (first in, first out queue) is used in the transmit path to compensate for any PPM (parts-per-million) differences between the transmit circuits and receiving circuits. Depending on packet size and the number of entries in the FIFO, a small variation in latency can be observed. (Note: When the PHY is used for precision-time protocol- (PTP-) based timestamping applications, the presence of the FIFO does not affect the accuracy of the timestamps. Future Proof with 1000BASE-T
Since the installation of industrial equipment and networks is capital-intensive, it is prudent to use a PHY device that can future-proof network speed requirements up to 1000BASE-T. The Marvell 88E1510P/1512P/1510Q family of PHY products supports 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T. The low latency ranges observed in 1000BASE-T mode is shown below.
Extended Temperature Operation and ESD support
Industrial motors and robots connected by an Ethernet network often have to weld metals at very high temperatures.
 This requires the PHY to operate in environments where the ambient temperature remains high throughout the entire duration of operation (for more than several hours). The Marvell 88E1510P/1512P/1510Q family of PHY products was designed to operate in ambient operating temperature ranges of minus -40 0C to 85 0C degrees (or 125 0C maximum junction temperature.)
This requires the PHY to operate in environments where the ambient temperature remains high throughout the entire duration of operation (for more than several hours). The Marvell 88E1510P/1512P/1510Q family of PHY products was designed to operate in ambient operating temperature ranges of minus -40 0C to 85 0C degrees (or 125 0C maximum junction temperature.) Packaging and Interface Options
The Marvell 88E1510P/1512P/1510Q family of PHYs is offered in 48-pin or 56-pin QFN packages. It also offers a variety of host interface options such as RGMII, MII and SGMII. For information on specific features, please review the attached product selector guide.
-
May 01, 2016
Marvell 通过 Linux 基金会项目支持企业级网络操作系统
By Yaniv Kopelman, Networking and Connectivity CTO, Marvell
White box switches are a “blank” standard hardware that relies on a network operating system, commonly Linux-based.
Built to run on Linux and open hardware, OpenSwitch is a full-featured network operating system (NOS) aimed at enabling the transition to disaggregated networks. OpenSwitch allows for freedom of innovation while maintaining stability and limiting vulnerability, and has a reliable architecture focused on modularity and availability.
This contribution to an industry standard NOS will enable Marvell devices to be widely used across different markets and boxes. To learn more, please visit: http://www.openswitch.net/, or read the full press release.
-
2016 年 5 月 15 日
全新的以太网收发器为 Cat5e 电缆上的更高数据速率提供更低成本解决方案
作者:Ron Cates,Marvell 联网业务部产品营销高级总监
 The first commercially available Ethernet Transceivers, the Alaska® 882010/40 family is fully optimized for 2.5Gbps and 5Gbps data rates over Cat5e cables. 该设备体积小功耗低,可完美搭配 Cat5e 以太网电缆之中的最常见安装类型,这类电缆一般用于 802.11 ac 接入点上行链路、交换机、服务器、工作站和高端 PC 等要求高速连接的应用。
The first commercially available Ethernet Transceivers, the Alaska® 882010/40 family is fully optimized for 2.5Gbps and 5Gbps data rates over Cat5e cables. 该设备体积小功耗低,可完美搭配 Cat5e 以太网电缆之中的最常见安装类型,这类电缆一般用于 802.11 ac 接入点上行链路、交换机、服务器、工作站和高端 PC 等要求高速连接的应用。Marvell's advanced Digital Signal Processing (DSP) technology makes possible the repurposing of existing low-cost Cat5e Ethernet cables for data rates as high as 5Gbps, saving the cost of rewiring. The Alaska 88E2010/40 transceivers may also be kitted with Marvell's broad range of switches that support 4 to 48 NBASE ports, providing a seamless system solution. 该设备还支持 Category 6、6a 和 7 类电缆,并支持各种各样的主机接口。 另外,Alaska 收发器系列以全面向后兼容线路侧的传统低速以太网性能为特色。 Other features include the incorporation of Marvell's advanced Virtual Cable Tester® technology for cable fault detections and proactive cable performance monitoring, and compliance with the emerging IEEE802.3bz standard and the NBASE-T Alliance specification for 2.5Gbps and 5Gpbs data rates over Cat5e cables. 另外,这款以太网收发器支持 100G-LR4 和 SR4 光模块,以及具备 2.5G/5G 性能的企业级交换机。
Alaska 88E2010/40 收发器扩展了 Alaska 产品套件,并提供多种附加功能和优势,非常适合使用以太网电缆的重要应用。
要了解更多信息,请下载产品简介:
-
February 11, 2015
Marvell 获得 Linley Group 2014 年度分析师选择奖
作者:Amit Avivi,Marvell 产品营销经理
 Linley Group 公布其年度分析师选择奖得主,Marvell 很荣幸分享大奖新闻:Marvell Prestera® 98DX4251 获选成为 2014 年杰出网络芯片。 Marvell Prestera 98DX4251 是 Marvell 的下一代数据包处理器,其设计专为支持实现性能和成本优化的解决方案,适合服务提供商和园区环境中的广泛平台。
Linley Group 公布其年度分析师选择奖得主,Marvell 很荣幸分享大奖新闻:Marvell Prestera® 98DX4251 获选成为 2014 年杰出网络芯片。 Marvell Prestera 98DX4251 是 Marvell 的下一代数据包处理器,其设计专为支持实现性能和成本优化的解决方案,适合服务提供商和园区环境中的广泛平台。Bob Wheeler 是 Linley Group 网络首席分析师,分享了选择 Marvell 作为获胜者的想法,“我们选择 Marvell 的 Prestera 98DX4251 数据包处理器作为最佳网络芯片,是因为其功能组将电信级以太网汇聚交换机的最先进技术又向前推动了一步。 通过提供五级电信级层次化 QoS 结合虚拟化和隧道能力,98DX4251 实现了下一代网络中接入和汇聚层高度差异化的服务交付。”
Linley Group 分析师选择奖分七个类别表彰 2014 年出众的半导体产品: PC/服务器处理器、移动处理器、嵌入式处理器、处理器-IP 内核、网络芯片、移动芯片,以及杰出技术。 Linley Group 的技术分析师团队会根据特定终端系统和市场的性能、功耗、功能和每设备成本的综合影响,衡量领先产品的优点。 请于此处查看更多 2014 年获奖信息。
Marvell 诚挚感谢 Linley Group 授予 Marvell 此项大奖,感谢其对先进处理器产品的肯定,这有助于促进行业创新性能的发展。
-
January 16, 2015
无需继续寻觅 - Marvell 突破性地将 Questflo 网络搜索引擎提升至 800 万个数据流
作者:Marvell 公关团队
According to Cisco Forecasts¹, in three years mobile data traffic is projected to hit 11.2 exabytes per month (1 exabyte = 1 billion gigabytes) and will experience a 66 percent Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from 2012 to 2017.
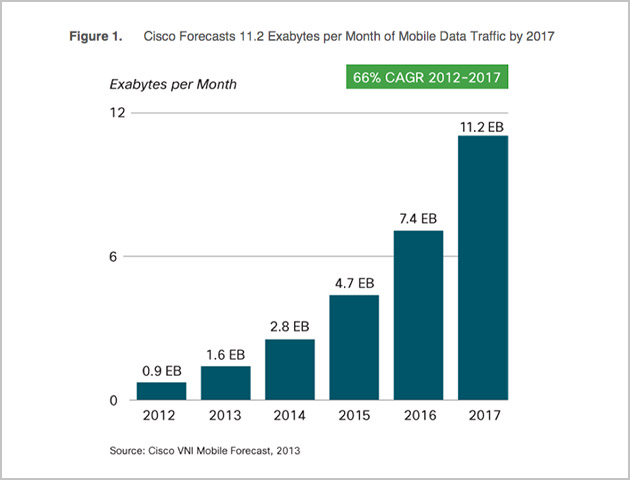 移动互联网和物联网 (IoT)、可穿戴设备、汽车互联是促进增长的原动力。 人均设备数量以及移动设备上运行的服务和应用程序数量都在逐渐增长。 例如,用户可以通过一部手机播放视频、访问社交网络或企业办公应用,或运行任何程序,同时还可拥有平板电脑和可穿戴设备(例如 iwatch,这些设备会产生更多流量)。 网络服务提供商和运营商提高服务水平质量和安全性的同时需要持续应对数据的爆炸式增长,因为用户的所有上述活动必须在某些点回程或聚集至云端。
移动互联网和物联网 (IoT)、可穿戴设备、汽车互联是促进增长的原动力。 人均设备数量以及移动设备上运行的服务和应用程序数量都在逐渐增长。 例如,用户可以通过一部手机播放视频、访问社交网络或企业办公应用,或运行任何程序,同时还可拥有平板电脑和可穿戴设备(例如 iwatch,这些设备会产生更多流量)。 网络服务提供商和运营商提高服务水平质量和安全性的同时需要持续应对数据的爆炸式增长,因为用户的所有上述活动必须在某些点回程或聚集至云端。当前基于三元内容可寻址存储器 (TCAM) 的解决方案无法满足未来带宽和服务的扩展需求,无法应对数据的爆炸式增长。 业界一直在尝试其他网络搜索引擎解决方案,还没有一个解决方案可在以下各方面都出类拔萃: 性能、密度、功耗、成本、尺寸和可靠性。 目前,基于 SRAM 的解决方案尚不能满足这些应用的性能需求,TCAM 增加了密度,但价格昂贵并且存在运行发热问题,无法满足功耗、热量要求以及这些网络系统的其他要求。
转发范式逐渐转移至基于流量的管理范式是另一个驱动力,在管理范式下,新的服务可能不是由 IPv4 或 Ipv6 方案驱动,而是由彼此独立的方案所驱动。 新的软件定义网络 (SDN) 和网络功能虚拟化 (NFV) 平台将要求在高容量、稳定的延迟和吞吐量下依然保持相当的灵活性,从而支持未来网络。
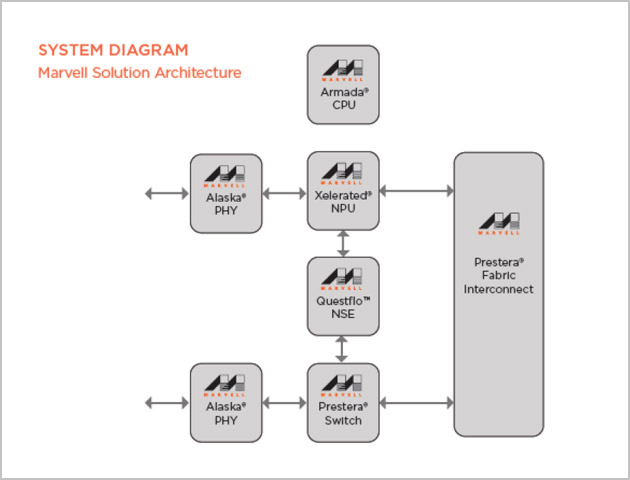
最近,Marvell 于 10 月 20 日推出 Marvell Questflo™ 98TX1100,同时宣布了一项重大技术突破,即开创性的基于静态随机存取存储器 (SRAM) 的网络搜索引擎,可以 1/3 的功耗提供 4 倍容量,从而满足下一代网络设备的需求。 Questflo 98Tx1100 专为运营商和企业服务/边缘路由器、安全设备、网路分流器、数据中心交换机、服务器、负载平衡器、新的 SDN 和 NFV 平台而设计,可扩展至 800 万个数据流,实现每秒 24 亿次搜索。 此外,Marvell 解决方案仅以 25W 典型功耗即可提供所需性能和密度。 Marvell 的全新网络搜索引擎与 Marvell Xelerated 400 Gbps 线速网络处理器产品和基于 ARM 的 ARMADA XP 嵌入式控制处理器组合后,可提供一套完整的解决方案架构,助力下一代设备提供商集中支持移动和物联网设备的指数级增长。
 The Linley Group 首席网络分析师 Bob Wheeler 这样形容 Marvell 的突破: “Marvell 正作为网络搜索技术的优选供应商占领市场,因为下一代网络设备正逐渐转向具有高度灵活性和高度可扩展性的基于流量的服务。 只有使用诸如 Questflo 这样革命性的新方案才能满足设计下一代新网络设备所要求的可扩展性数量级。”
The Linley Group 首席网络分析师 Bob Wheeler 这样形容 Marvell 的突破: “Marvell 正作为网络搜索技术的优选供应商占领市场,因为下一代网络设备正逐渐转向具有高度灵活性和高度可扩展性的基于流量的服务。 只有使用诸如 Questflo 这样革命性的新方案才能满足设计下一代新网络设备所要求的可扩展性数量级。”By addressing the needs of next-generation networking equipment on all fronts - performance, density, power, cost, form factor and reliability – we believe the search for the next-generation search engine is over, the answer is Questflo.
¹指 Cisco 可视化网络指数: 2012–2017 年全球移动数据流量预测更新,© 2013 Cisco
最近推文
- HashiCorp and Marvell: Teaming Up for Multi-Cloud Security Management
- Cryptomathic and Marvell: Enhancing Crypto Agility for the Cloud
- The Big, Hidden Problem with Encryption and How to Solve It
- Self-Destructing Encryption Keys and Static and Dynamic Entropy in One Chip
- Dual Use IP: Shortening Government Development Cycles from Two Years to Six Months